t5学习笔记
t5是google ai在2020年发布的一个模型,它可以进行任意text2text的任务,并且可以支持multitask learning. 本文会用t5做一些试验。这些试验都在colab中运行。这里的代码参考了t5的官方例子
Setup
这里安装了t5所需要的依赖,并配置了一个免费的TPU.
- 创建一个GCP Project,并配置一个GCS bucket.
- Colab中 Runtime -> Change Runtime Type, 选择TPU Runtime
这里colab选择的tf版本是2.0,主要是为了在eager mode下连接TPU,并让TPU worker可以写gcs. t5目前基于tf1, 所以之后的代码全部是在tf1下运行的. 过程中会弹出一个验证框,登录google账号并输入验证码就可以了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
GCS_BUCKET = 'your_gcs_bucket_name'
%tensorflow_version 2.x
!pip install -q t5
import functools
import os
import time
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=DeprecationWarning)
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import t5
BASE_DIR = f"gs://{GCS_BUCKET}/t5"
DATA_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "data")
MODELS_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "models")
print("Setting up GCS access...")
import tensorflow_gcs_config
from google.colab import auth
# Set credentials for GCS reading/writing from Colab and TPU.
TPU_TOPOLOGY = "v2-8"
try:
tpu = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver() # TPU detection
TPU_ADDRESS = tpu.get_master()
print('Running on TPU:', TPU_ADDRESS)
except ValueError:
raise BaseException('ERROR: Not connected to a TPU runtime; please see the previous cell in this notebook for instructions!')
auth.authenticate_user()
tf.config.experimental_connect_to_host(TPU_ADDRESS)
tensorflow_gcs_config.configure_gcs_from_colab_auth()
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
# Improve logging.
from contextlib import contextmanager
import logging as py_logging
tf.get_logger().propagate = False
py_logging.root.setLevel('INFO')
@contextmanager
def tf_verbosity_level(level):
og_level = tf.logging.get_verbosity()
tf.logging.set_verbosity(level)
yield
tf.logging.set_verbosity(og_level)
Data
这里用的数据集来自Quora的一个比赛: https://www.kaggle.com/c/quora-question-pairs 比赛中给定两个quora questions, 模型需要判断这两个问题是否具有相同的意义。例如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
q1: how i can be good at handwriting?
q2: how can i have good handwriting?
output: 1
q1: tea: is it dangerous to boil water in a plastic electric kettle?
q2: why should we avoid hot tea in plastic cup?
output: 0
虽然用t5来解决这么一个问题有点杀鸡用牛刀了,但是我一时间没找到什么有意思的问题,所以就先拿这个试试。
training set有40万行data, test set有几百万行,因为有很多example是自动生成的,这些example并不会参与最终的score计算,只是为了防止作弊设置的。
下载kaggle data:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
%%bash
pip install kaggle
mkdir -p ~/.kaggle
echo '{"username":"your_kaggle_username","key":"your_kaggle_api_key"}' > ~/.kaggle/kaggle.json
chmod 600 ~/.kaggle/kaggle.json
kaggle competitions download -c quora-question-pairs
unzip test.csv.zip
unzip train.csv.zip
unzip sample_submission.csv.zip
接下来我们从kaggle data生成tfrecord. 虽然tensorflow也可以直接解析csv文件,但是1
tf.decode_csv
我们从原来的1
train.csv
1
train.tfrecord
1
validation.tfrecord
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
VALIDATION_PERCENT = 0.1
def to_tf_example(split, values):
def to_str_feature(v):
return [str(v).encode('utf-8')]
if split in ('train', 'validation'):
features = {
'id': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=to_str_feature(values['id']))),
'question1':
tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=to_str_feature(values['question1']))),
'question2':
tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=to_str_feature(values['question2']))),
'is_duplicate':
tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=to_str_feature(values['is_duplicate']))),
}
else:
features = {
'test_id': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=to_str_feature(values['test_id']))),
'question1':
tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=to_str_feature(values['question1']))),
'question2':
tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=to_str_feature(values['question2']))),
}
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature=features))
return example
print('Writing train/valid tfrecords...')
train_df = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
with tf.io.TFRecordWriter('train.tfrecord') as train_writer, \
tf.io.TFRecordWriter('validation.tfrecord') as validation_writer:
for _idx, row in train_df.iterrows():
example = to_tf_example('train', row)
if np.random.rand() < VALIDATION_PERCENT:
writer = validation_writer
else:
writer = train_writer
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
print('Writing test tfrecords...')
test_df = pd.read_csv('test.csv')
with tf.io.TFRecordWriter('test.tfrecord') as test_writer:
for _idx, row in test_df.iterrows():
example = to_tf_example('test', row)
test_writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
以下是1
train.csv

接下来把生成的tfrecord都copy到gcs上:
1
2
3
qp_data_base_dir = DATA_DIR + '/quora-question-pairs'
print('copy tfrecord files to GCS:', qp_data_base_dir)
!gsutil cp *.tfrecord {qp_data_base_dir}
Register T5 data Task
t5是一个text to text model,所以input和ouput都是text,而具体的格式可以自由设计。在这个问题中,我们的设计如下:
1
2
Input: is duplicate: <question 1> <SEP> <question 2>
Output: 0 或 1
接下来,我们需要把这个训练任务注册到t5中。在任务中我们指定一个dataset_fn和一个text_preprocessor. 在后面我们可以看到,可以用同一个dataset加不同的preprocessor来训练不同的任务,非常方便。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
def qp_dataset_fn(split, shuffle_files=False):
del shuffle_files # unused
assert split in ('train', 'validation', 'test'), "Invalid split"
ds = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(f'{DATA_DIR}/quora-question-pairs/{split}.tfrecord')
def parse_example(example_proto):
feature_description = {
'question1': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string, default_value=''),
'question2': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string, default_value=''),
'is_duplicate': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string, default_value=''),
}
return tf.io.parse_single_example(example_proto, feature_description)
ds = ds.map(
parse_example,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
return ds
print('examples from train:')
for ex in tfds.as_numpy(qp_dataset_fn("train").take(5)):
print(ex)
print('examples from test:')
for ex in tfds.as_numpy(qp_dataset_fn("test").take(5)):
print(ex)
def qp_preprocessor(ds):
def normalize_text(text):
"""Lowercase and remove quotes from a TensorFlow string."""
text = tf.strings.lower(text)
text = tf.strings.regex_replace(text,"'(.*)'", r"\1")
return text
def to_inputs_and_targets(ex):
return {
"inputs":
tf.strings.join(
["is duplicate: ", normalize_text(ex["question1"]), " <SEP> ", normalize_text(ex["question2"])]),
"targets": ex["is_duplicate"]
}
return ds.map(to_inputs_and_targets,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
t5.data.TaskRegistry.add(
"qp_is_duplicate",
# Supply a function which returns a tf.data.Dataset.
dataset_fn=qp_dataset_fn,
splits=["train", "validation", "test"],
# Supply a function which preprocesses text from the tf.data.Dataset.
text_preprocessor=[qp_preprocessor],
# Lowercase targets before computing metrics.
postprocess_fn=t5.data.postprocessors.lower_text,
# We'll use accuracy as our evaluation metric.
metric_fns=[t5.evaluation.metrics.accuracy],
# Not required, but helps for mixing and auto-caching.
# num_input_examples=num_nq_examples
)
qp_task = t5.data.TaskRegistry.get("qp_is_duplicate")
ds = qp_task.get_dataset(split="validation", sequence_length={"inputs": 128, "targets": 5})
print("A few preprocessed validation examples...")
for ex in tfds.as_numpy(ds.take(5)):
print(ex)
可以从输出中看到1
qp_task
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
A few preprocessed validation examples...
{'inputs_plaintext': b'is duplicate: how can one overcome the fear of speaking in public? <SEP> how could we overcome the fear of speaking truth?', 'inputs': array([ 19, 19197, 10, 149, 54, 80, 8269, 8, 2971,
13, 4461, 16, 452, 58, 3, 2, 134, 8569,
3155, 149, 228, 62, 8269, 8, 2971, 13, 4461,
2827, 58, 1]), 'targets_plaintext': b'0', 'targets': array([ 3, 632, 1])}
{'inputs_plaintext': b'is duplicate: how i can be good at handwriting? <SEP> how can i have good handwriting?', 'inputs': array([ 19, 19197, 10, 149, 3, 23, 54, 36, 207,
44, 609, 9933, 58, 3, 2, 134, 8569, 3155,
149, 54, 3, 23, 43, 207, 609, 9933, 58,
1]), 'targets_plaintext': b'1', 'targets': array([209, 1])}
...
需要注意的是,虽然我们的output是0或1,但是不能把output sequence length设成1,因为output是sentence piece, 从以上输出中看长度是3和2,所以设置一个大于3的值应该没问题。
Model
接下来我们开始模型训练。这个模型从1
pretrained_model_dir
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
def get_model(task_name, model_size="3B"):
model_size = "3B" # ["small", "base", "large", "3B", "11B"]
# Public GCS path for T5 pre-trained model checkpoints
BASE_PRETRAINED_DIR = "gs://t5-data/pretrained_models"
pretrained_model_dir = os.path.join(BASE_PRETRAINED_DIR, model_size)
model_dir = os.path.join(MODELS_DIR, task_name, model_size)
# Set parallelism and batch size to fit on v2-8 TPU (if possible).
# Limit number of checkpoints to fit within 5GB (if possible).
model_parallelism, train_batch_size, keep_checkpoint_max = {
"small": (1, 256, 16),
"base": (2, 128, 8),
"large": (8, 64, 4),
"3B": (8, 16, 1),
"11B": (8, 16, 1)}[model_size]
tf.io.gfile.makedirs(model_dir)
# The models from our paper are based on the Mesh Tensorflow Transformer.
model = t5.models.MtfModel(
model_dir=model_dir,
tpu=TPU_ADDRESS,
tpu_topology=TPU_TOPOLOGY,
model_parallelism=model_parallelism,
batch_size=train_batch_size,
sequence_length={"inputs": 128, "targets": 5},
learning_rate_schedule=0.003,
save_checkpoints_steps=5000,
keep_checkpoint_max=keep_checkpoint_max,
iterations_per_loop=100,
)
return model, pretrained_model_dir, model_dir
model, pretrained_dir, model_dir = get_model('qp_is_duplicate')
model.finetune(
mixture_or_task_name="qp_is_duplicate",
pretrained_model_dir=pretrained_dir,
finetune_steps=25000 # 1 epoch ~= 25000 steps
)
接下来我们在validation set上去看效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Use a larger batch size for evaluation, which requires less memory.
model.batch_size = 64
model.eval(
mixture_or_task_name="qp_is_duplicate",
checkpoint_steps="all",
split="validation"
)
output:
1
2
...
INFO:tensorflow:eval/qp_is_duplicate/accuracy at step 1025000: 90.693
可以看到accuracy达到了90.69%.
原比赛衡量标准是logloss, 但是因为我们直接输出0或1,没法直接比较。我查看了一下讨论,排在11th的选手accuracy大约在0.87(threshold=0.5) / 0.91(best threshold)左右。
https://www.kaggle.com/c/quora-question-pairs/discussion/33187
所以,在没有做任何特征工程,数据分析的情况下,我们只训练一个epoch,并且还没有用上全部数据,validation上的效果已经接近这个比赛的top水平了。
Multi-task training
只做一个classification太简单了,接下来我们尝试另一个更有意思的问题。我们来考虑另一个任务:给定一个问题,我们想直接生成一个相同意思,但是表达不同的问题。例如:
1
2
Input: what is the proper way to run long distance compared to that of short distance?
Output: what is proper long distance running form?
我们可以利用之前的dataset, 把label为1的样本拿出来做训练。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
def gsq_dataset_fn(split, shuffle_files=False):
del shuffle_files # unused
assert split in ('train', 'validation'), "Invalid split"
ds = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(f'{DATA_DIR}/quora-question-pairs/{split}.tfrecord')
def parse_example(example_proto):
feature_description = {
'question1': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string, default_value=''),
'question2': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string, default_value=''),
'is_duplicate': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string, default_value=''),
}
return tf.io.parse_single_example(example_proto, feature_description)
ds = ds.map(
parse_example,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
ds = ds.filter(lambda ex: tf.equal(ex['is_duplicate'], tf.constant(b'1')))
return ds
print('examples from train:')
for ex in tfds.as_numpy(gsq_dataset_fn("train").take(5)):
print(ex)
def gsq_preprocessor(ds):
def normalize_text(text):
"""Lowercase and remove quotes from a TensorFlow string."""
text = tf.strings.lower(text)
text = tf.strings.regex_replace(text,"'(.*)'", r"\1")
return text
def to_inputs_and_targets(ex):
return {
"inputs":
tf.strings.join(
["generate similar question: ", normalize_text(ex["question1"])]),
"targets": normalize_text(ex["question2"])
}
return ds.map(to_inputs_and_targets,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
t5.data.TaskRegistry.add(
"generate_similar_question",
# Supply a function which returns a tf.data.Dataset.
dataset_fn=gsq_dataset_fn,
splits=["train", "validation"],
# Supply a function which preprocesses text from the tf.data.Dataset.
text_preprocessor=[gsq_preprocessor],
# Lowercase targets before computing metrics.
postprocess_fn=t5.data.postprocessors.lower_text,
# We'll use accuracy as our evaluation metric.
metric_fns=[t5.evaluation.metrics.accuracy],
# Not required, but helps for mixing and auto-caching.
# num_input_examples=num_nq_examples
)
qp_task = t5.data.TaskRegistry.get("generate_similar_question")
ds = qp_task.get_dataset(split="validation", sequence_length={"inputs": 128, "targets": 128})
print("A few preprocessed validation examples...")
for ex in tfds.as_numpy(ds.take(5)):
print(ex)
这里的代码跟之前非常相像,没什么可说的,区别主要在input中换了一个任务名,并且output sequence length不一样了。
接下来,我们可以不只训练这一个任务,我们可以把这个任务和之前的任务一起训练:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
t5.data.MixtureRegistry.remove('qp_all')
t5.data.MixtureRegistry.add(
"qp_all",
["qp_is_duplicate", "generate_similar_question"],
default_rate=1.0
)
mixed_task = t5.data.MixtureRegistry.get("qp_all")
ds = mixed_task.get_dataset(split="validation", sequence_length={"inputs": 128, "targets": 128})
print("A few mixed task validation examples...")
for ex in tfds.as_numpy(ds.take(10)):
print(ex)
这里我们生成了一个mixed task, 把两个任务混合到一起。这是t5的强大之处,因为可以支持任意的input格式,所以可以把不同的任务放在一起训练。
接下来训练模型:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
task_name = 'qp_all'
model_size = "3B" # ["small", "base", "large", "3B", "11B"]
# Public GCS path for T5 pre-trained model checkpoints
BASE_PRETRAINED_DIR = "gs://t5-data/pretrained_models"
pretrained_model_dir = os.path.join(BASE_PRETRAINED_DIR, model_size)
model_dir = os.path.join(MODELS_DIR, task_name, model_size)
# Set parallelism and batch size to fit on v2-8 TPU (if possible).
# Limit number of checkpoints to fit within 5GB (if possible).
model_parallelism, train_batch_size, keep_checkpoint_max = {
"small": (1, 256, 16),
"base": (2, 128, 8),
"large": (8, 64, 4),
"3B": (8, 16, 1),
"11B": (8, 16, 1)}[model_size]
tf.io.gfile.makedirs(model_dir)
# The models from our paper are based on the Mesh Tensorflow Transformer.
model = t5.models.MtfModel(
model_dir=model_dir,
tpu=TPU_ADDRESS,
tpu_topology=TPU_TOPOLOGY,
model_parallelism=model_parallelism,
batch_size=train_batch_size,
sequence_length={"inputs": 128, "targets": 128},
learning_rate_schedule=0.003,
save_checkpoints_steps=5000,
keep_checkpoint_max=keep_checkpoint_max,
iterations_per_loop=100,
)
model.finetune(
mixture_or_task_name="qp_all",
pretrained_model_dir=pretrained_model_dir,
finetune_steps=25000 # 1 epoch ~= 25000 steps
)
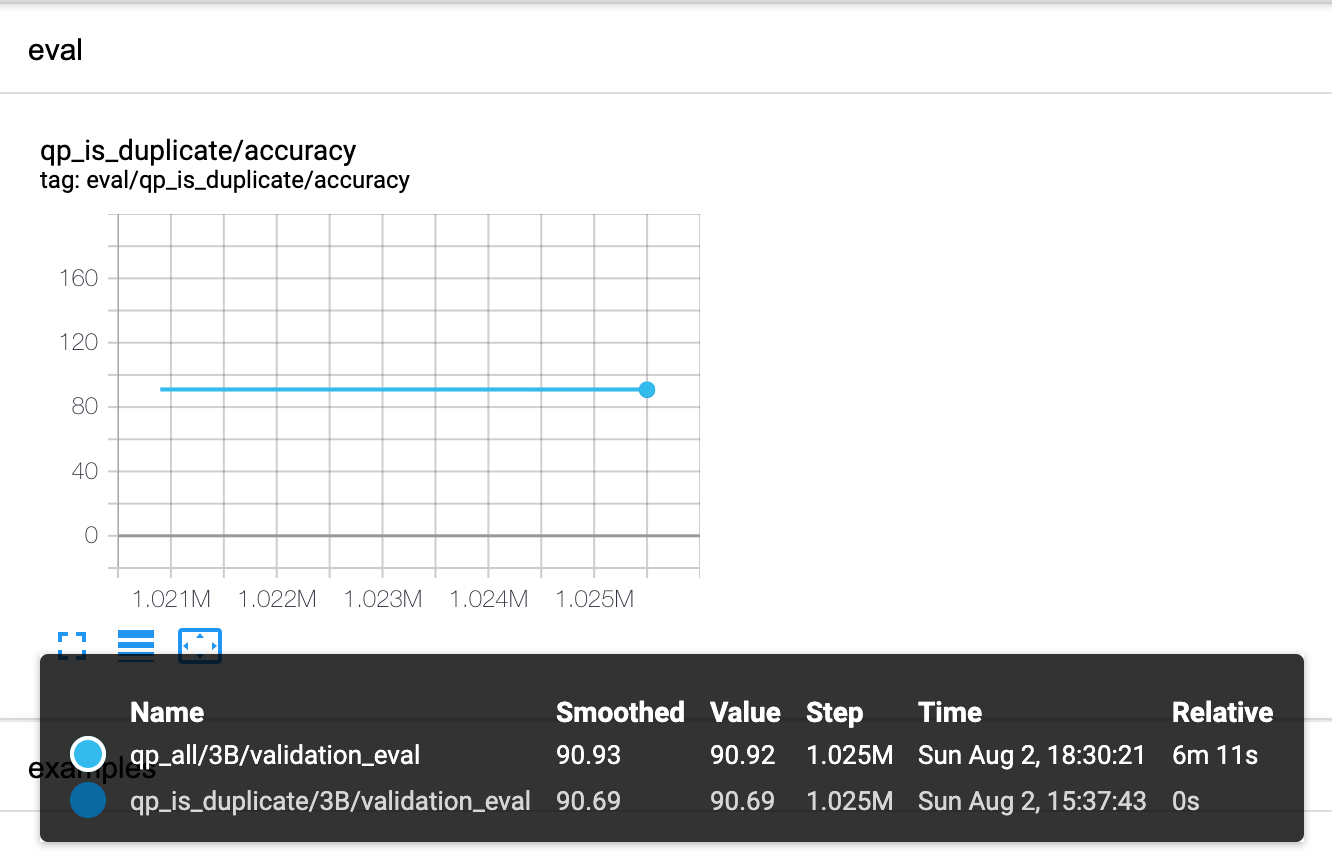
然后我们再evaluate. 注意,我们训练了两个任务,但是evaluate仍然只evaluate第一个任务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Use a larger batch size for evaluation, which requires less memory.
model.batch_size = 64
model.eval(
mixture_or_task_name="qp_is_duplicate",
checkpoint_steps="all",
split="validation"
)
可以看到,在只训练了半个epoch的情况下(因为step没变, 从一个task变成两个)accuracy甚至从90.6%上升到了90.93%。
接下来,我们可以测试下模型是不是真的可以同时学会两个任务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
now = time.time()
questions = [
"is duplicate: how have you simplified your life? <SEP> how do i simplify my messed up life?",
"is duplicate: Astrology: I am a Capricorn Sun Cap moon and cap rising...what does that say about me? <SEP> I'm a triple Capricorn (Sun, Moon and ascendant in Capricorn) What does this say about me?",
"is duplicate: How do I read and find my YouTube comments? <SEP> How can I see all my Youtube comments?",
"generate similar question: how have you simplified your life?",
"generate similar question: I am a Capricorn Sun Cap moon and cap rising...what does that say about me?",
"generate similar question: How do I read and find my YouTube comments?"
]
# Write out the supplied questions to text files.
predict_inputs_path = os.path.join(model_dir, "predict_inputs_%d.txt" % now)
predict_outputs_path = os.path.join(model_dir, "predict_outputs_%d.txt" % now)
# Manually apply preprocessing by prepending "triviaqa question:".
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(predict_inputs_path, "w") as f:
for q in questions:
f.write(q.lower() + '\n')
# Ignore any logging so that we only see the model's answers to the questions.
with tf_verbosity_level('ERROR'):
model.batch_size = 8 # Min size for small model on v2-8 with parallelism 1.
model.predict(
input_file=predict_inputs_path,
output_file=predict_outputs_path,
# Select the most probable output token at each step.
temperature=0,
)
# The output filename will have the checkpoint appended so we glob to get
# the latest.
prediction_files = sorted(tf.io.gfile.glob(predict_outputs_path + "*"))
print("\nPredictions using checkpoint %s:\n" % prediction_files[-1].split("-")[-1])
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(prediction_files[-1]) as f:
for q, a in zip(questions, f):
if q:
print("Q: " + q)
print("A: " + a)
print()
output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
Predictions using checkpoint 1025000:
Q: is duplicate: how have you simplified your life? <SEP> how do i simplify my messed up life?
A: 1
Q: is duplicate: Astrology: I am a Capricorn Sun Cap moon and cap rising...what does that say about me? <SEP> I'm a triple Capricorn (Sun, Moon and ascendant in Capricorn) What does this say about me?
A: 1
Q: is duplicate: How do I read and find my YouTube comments? <SEP> How can I see all my Youtube comments?
A: 1
Q: generate similar question: how have you simplified your life?
A: what are some ways to simplify your life?
Q: generate similar question: I am a Capricorn Sun Cap moon and cap rising...what does that say about me?
A: i am a capricorn sun, cap moon and cap rising. what does that say about me?
Q: generate similar question: How do I read and find my YouTube comments?
A: how do i read my youtube comments?
可以看到,模型真的学会了两个任务: 当你问is_duplicate的时候,它知道要输出0或1,而当你问generate similar question的时候,它会去生成一个相似的问题,非常的神奇。